在前面的两篇博客中我们看到,无论是实现一个 http 模块,或者是 http filter 模块,都需要实现模块自己的 ngx_http_module_t 结构体。
typedef struct {
ngx_int_t (*preconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
ngx_int_t (*postconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
void *(*create_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
char *(*init_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *conf);
void *(*create_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
char *(*merge_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
void *(*create_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
char *(*merge_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
} ngx_http_module_t;
其中 main、srv、loc 分别对应 nginx.conf 中的 http,server,location 配置块,本文就来关注一下这些配置项是如何被解析和使用的。
解析 http 不同级别配置项
一个简单的 nginx.conf 配置如下:
http {
test_cmd;
server {
listen 80;
test_cmd;
location / {
test_cmd;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
可以看到,在 http,server,location 三个配置块中都有我们自定义模块的命令 test_cmd。
对于 nginx http 框架而言,在解析 main 级别的配置项时,必须同时创建3个结构体,用于合并之后会解析到的 server,location 配置项。换句话说:
- main 配置项,create_main_conf、srv、loc 三个函数都要被调用一次,返回3个结构体。
- server 配置项, srv、loc 两个函数都要被调用一次。
- location 配置项,loc 函数被调用一次。
在 http 框架处理到某个阶段时,例如在寻找到合适的 location 前,如果试图去取某个模块的配置结构体,将会得到 server 级别的配置,而如果寻找到 location 之后,就会得到 location 结构下的配置。
main 级别配置项
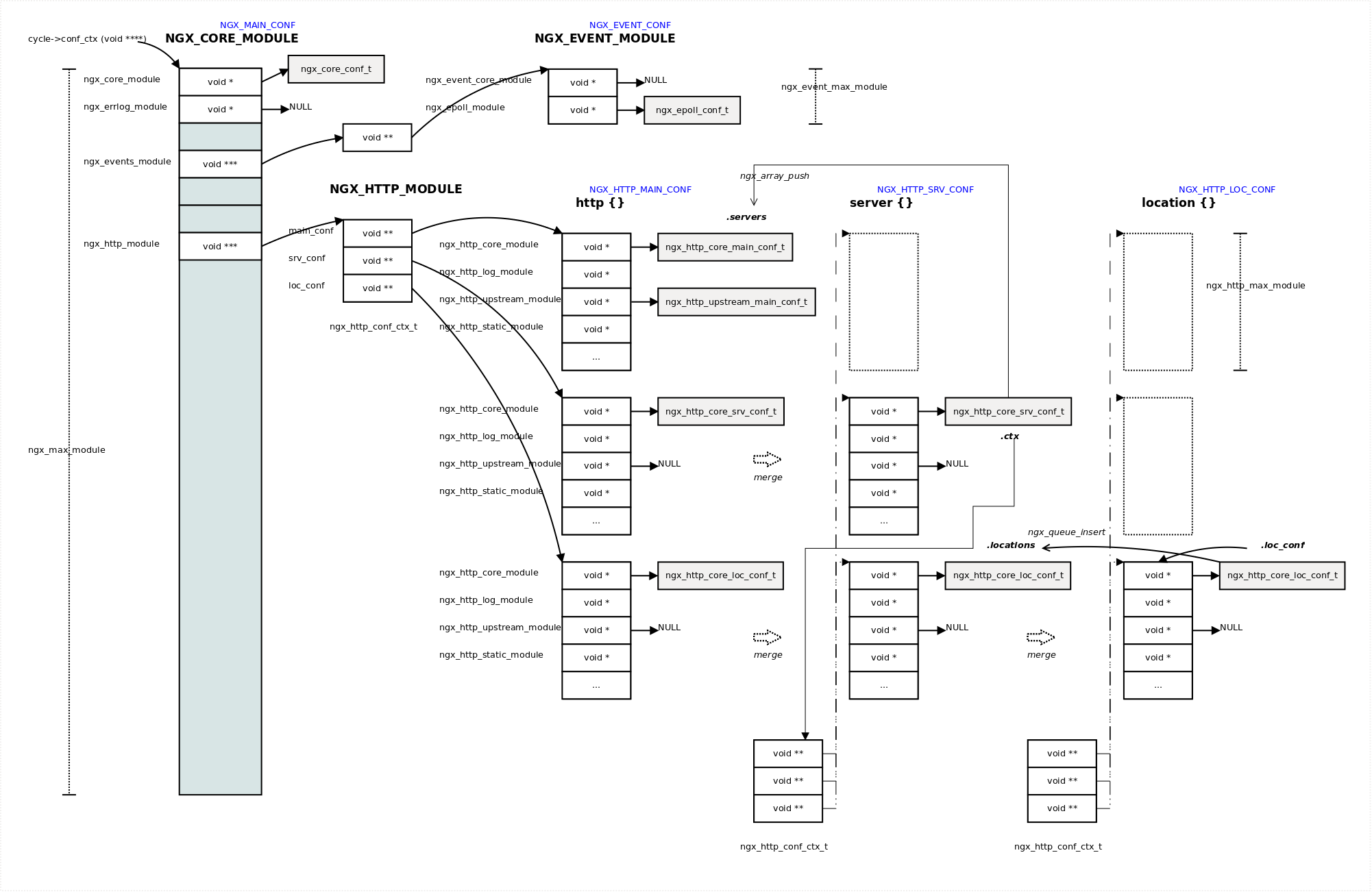
所有和 http 相关模块的配置都放在 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体中,先来看一下有个大概印象
typedef struct {
void **main_conf;
void **srv_conf;
void **loc_conf;
} ngx_http_conf_ctx_t;
回顾本文一开头提到,如果一个模块定义了自己的处理函数,那么通过这些函数生成的结构体(一块内存区域)地址将会存到ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 中。例如
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t
ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t
在《深入理解 nginx》P354 有详细介绍,还有一张 Just Carry On 的配图也不错。
 {:height=“500” width=“600”}
{:height=“500” width=“600”}
说完了所有有关 http 模块配置结构存放位置,再来看一下对于整个 nginx 来说,这一块http 的配置又放在哪呢?还是看上图,在 ngx_cycle_t 的 conf_ctx 中。
src/core/ngx_cycle.c 中 ngx_init_cycle() 函数关于调用 core module 的 create_conf 函数代码,先判断是不是 core module, 如果是则继续,否则跳过。
for (i = 0; cycle->modules[i]; i++) {
if (cycle->modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = cycle->modules[i]->ctx;
if (module->create_conf) {
rv = module->create_conf(cycle);
if (rv == NULL) {
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
cycle->conf_ctx[cycle->modules[i]->index] = rv;
}
}
我们可以尝试在 for 循环体的开始或最后分别打印模块名,如果放在最后打印,则可以看到这样的结果
ngx_core_module
ngx_errlog_module
ngx_regex_module
ngx_events_module
ngx_http_module
说明这些模块是所谓的 core module。而如果放在一开始,会看到一大堆输出,表示 nginx 默认编译进可执行文件的所有模块,而且内容与 obj/ngx_modules.c 先后顺序一致。
server 级别配置项
解析到 server 配置项时,也要创建 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体,其中 main_conf 指向上级 http 配置项,然后调用所有 http 模块的 create_srv_conf 函数和 create_loc_conf 函数,将返回的结构体指针存到 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 中。
以 http core module 模块为例,
结构体 ngx_http_core_main_conf_t 指针将存到 main_conf 数组里
结构体 ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t 指针将存到 srv_conf 数组里
结构体 ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t 指针将存到 loc_conf 数组里
location 级别配置项
location 配置项基本与上面两个类似,关于 location 和 server 的内存分布关系,参考 《深入理解 nginx》 P360-362